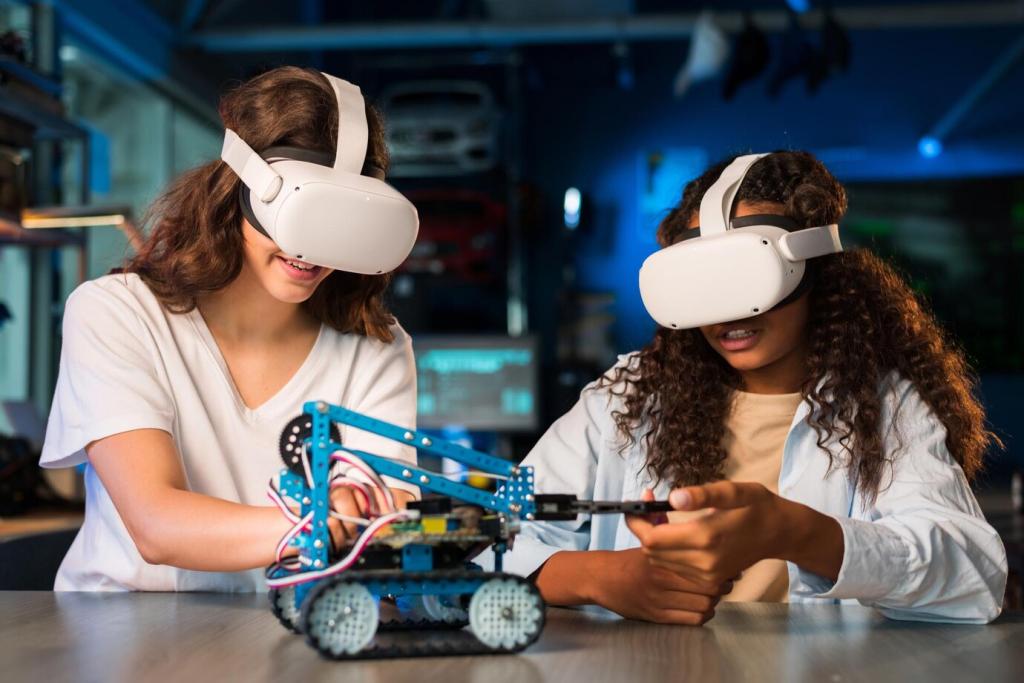
Chosen theme: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Concepts. Welcome to an inviting gateway into AI—clear, warm, and practical. We will demystify core ideas, share relatable stories, and offer simple next steps. Curious? Subscribe, leave questions, and tell us what you most want to learn next.
What AI Is (and Is Not)
A simple definition of AI
Artificial intelligence is about building systems that perform tasks requiring intelligence when done by humans, such as recognizing patterns, making decisions, and learning from data. Instead of magic, think careful design, measurable goals, and methods that improve with better data and feedback.
Narrow AI versus General AI
Today’s AI is narrow: models excel at specific tasks like translation, image tagging, or recommendations. General AI, which would flexibly reason across many domains, remains a research aspiration. Keep this distinction in mind to evaluate headlines, and comment with examples of narrow AI you already use daily.
A small orchard anecdote to make it real
A reader once shared how a simple camera and code sorted apples by color and size for a local orchard. It was not perfect, but it saved hours each week. That modest system captured AI’s spirit: define a task, collect data, learn patterns, and improve iteratively with real feedback.
Data teaches models what matters. Quality, quantity, and diversity shape how well systems generalize. Labels guide supervised learning, while unlabeled data powers discovery. If you are just starting, practice collecting small, clean datasets; then share your data challenges and we will suggest practical improvement tips.

Machine Learning at a Glance
01
With labeled examples, supervised learning maps inputs to outputs: spam or not spam, dog or cat, positive or negative sentiment. It thrives when labels are reliable and plentiful. Think about a classification you do often; what features would you label, and how would you measure success objectively?
02
Unsupervised learning reveals structure without labels—clustering customers, compressing images, or uncovering topics in text. It is fantastic for exploration and hypothesis generation. Have you tried grouping your notes or photos? Share a small experiment you could run this week and we will suggest tools.
03
Reinforcement learning trains agents to act by rewarding good choices and discouraging poor ones. Think game-playing bots or warehouse robots optimizing routes. Success depends on clever reward design and safe exploration. If you could reward a habit in your life, what metric would guide steady improvement?


Neural Networks and Deep Learning
A neural network layer computes weighted sums of inputs and passes them through nonlinear activations. This simple mechanism, repeated across layers, models complex relationships. Picture a chorus of tiny decision-makers combining votes. Curious about activation choices? Comment which functions you have seen and why they matter.
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
Early layers learn simple patterns; deeper layers compose them into richer concepts. In images, edges grow into textures, then objects. In language, characters build words, then meaning. This hierarchy explains deep learning’s power. Share an example where layered understanding helps you learn a skill outside technology.
Reasoning, Knowledge, and Planning
Symbolic systems represent facts and rules explicitly, enabling transparent reasoning and explanations. Knowledge graphs connect entities and relationships to support search and question answering. Combining these ideas with learned embeddings can improve relevance. Have a domain you know well? Sketch a tiny knowledge graph and share it.
From route planning to puzzle solving, search explores possibilities efficiently using heuristics. Classic algorithms like A* and breadth-first search remain foundational. Even simple heuristics can transform performance. Consider a daily decision, like scheduling; how might you define states, actions, and a heuristic to guide choices?
Hybrid approaches integrate neural networks for perception with symbolic components for logic, constraints, or guarantees. The result aims for accuracy plus interpretability. Imagine vision detecting objects while rules ensure safety. Interested in a beginner project? Comment, and we will outline a tiny hybrid demo you can try.
Ethics, Bias, and Trust in AI
Models can inherit biases from data or design choices, harming marginalized groups. Mitigation includes better sampling, fairness metrics, diverse evaluation, and inclusive practices. Ask how your system could fail, and who might be affected. Post a scenario, and we will discuss fairness strategies suited to it.